Google Classroom
Google Classroom is a free learning management system (LMS) developed by Google, designed to help teachers create, distribute, and manage classroom activities digitally. It integrates with Google Workspace tools like Docs, Drive, Meet, and Slides. It is one place for organizing assignments, resources, announcements, and feedback in K-12 classrooms.
(Google Classroom Workflow and Organization Tips and Tricks, 2020)
User Engagement:
In Google Classroom, students engage by submitting assignments, accessing course materials, collaborating on group work, and communicating with both teachers and peers. Teachers use the platform to post assignments, schedule announcements, grade student work, provide individualized feedback, and organize instructional materials into topic-based threads for clarity and accessibility. Parents stay informed and involved through guardian email summaries, which highlight missing work, upcoming assignments, and important teacher announcements, helping them remain connected to their child's academic progress.
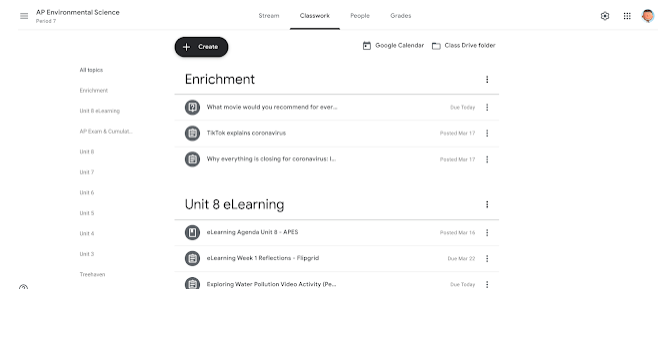
(Google Classroom Workflow and Organization Tips and Tricks, 2020)
Influence on Communication:
Google Classroom changes the way teachers and students communicate by providing an organized and flexible space to interact. Instead of just talking face-to-face, most communication happens through comments, private messages, and announcements. This makes it easier to keep track of important information and saves a record of everything shared. However, if there are too many messages and updates, it can get confusing or overwhelming, and some important things might be missed.
Information Consumption:
Google Classroom is able to have all the materials that teachers share, like links, PDFs, slides, and videos, in one place. This makes it easier for students to find and use everything they need for class. The stream layout helps students stay updated and encourages them to join in discussions with classmates. While this can help keep students engaged, it can also lead to feeling overwhelmed by too much information.
Impact on learning:
Google Classroom has a significant impact on learning by making educational resources and communication more accessible and organized. It allows students to easily access assignments, materials, and feedback all in one place, which helps them stay on track and manage their learning more independently. The platform also encourages collaboration through comments and discussions, which can deepen understanding and engagement. However, its effectiveness depends on how well students and teachers use it, strong self-management skills are needed, and challenges like digital access can affect how well students benefit. Overall, Google Classroom supports a more flexible and connected learning experience.
Safety:
Google for Education complies with the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) and the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), providing a secure, ad-free environment when used through a school domain. Teachers can control posting permissions, and students are not able to share outside of the classroom unless allowed.
Required Literacies:
To use Google Classroom effectively, students need to develop several important literacies. Digital literacy involves knowing how to navigate tabs and links, upload assignments, and use integrated tools like Google Docs, Slides, and Forms. Information literacy is also essential, as students must be able to tell the difference between reliable and unreliable sources, understand assignment instructions, and make sense of the digital materials shared in the platform. In addition, time management and organizational literacy help students stay on track by using features like the “To-Do” list, calendar, and Classwork tab to manage deadlines and prioritize tasks. Finally, communication literacy is important for engaging in clear and respectful written conversations, whether in public comment threads or private messages with teachers.
Reflect on Implications:
Google Classroom directly supports blended and remote learning models, allowing teachers to extend learning beyond the school day and support diverse learners with flexible access. It encourages routine digital interaction, making students more adept at managing digital workflows, an important skill for college and career readiness (Trust & Whalen, 2020). Parents can act as partners in learning by checking summaries and guiding their children in staying on task and organized.
Padlet
I have used Padlet a limited number of times, but after researching and learning about it, I am going to dive deeper into it and figure out a way to use it with my students next year. My student created their own group chat using their phones. I think this would help them out a lot more.
Overview:
Padlet is a digital collaboration platform that functions like a virtual bulletin board. Teachers and students use it to share text, images, videos, audio, and links on a scrollable canvas. It’s widely used in K-12 classrooms for brainstorming, feedback, reflections, digital storytelling, and group projects.
 (How To Use Padlet And 5 Ways To Implement It Into Your Classroom - ClassPoint Blog, 2023)
(How To Use Padlet And 5 Ways To Implement It Into Your Classroom - ClassPoint Blog, 2023)
User Engagement:
Students use Padlet to post responses to prompts, upload multimedia, comment on their classmates’ posts, and create digital portfolios that showcase their learning. Teachers can setup boards or walls for lessons, model responses, share resources, and give feedback through comments to guide students. When parents are given access, they can view their child’s work and class discussions, helping them stay informed and involved in thier child’s education.
 (How To Use Padlet And 5 Ways To Implement It Into Your Classroom - ClassPoint Blog, 2023)
(How To Use Padlet And 5 Ways To Implement It Into Your Classroom - ClassPoint Blog, 2023)
Influence on Communication:
Padlet encourages communication through visuals, writing, and audio, moving beyond just text, encouraging discussions to allow for multiple ways of expressing ideas. Students can use emojis, leave comments, record voice notes, and work together on timelines or maps. This makes classroom communication more engaging and accessible, creating a livelier and more inclusive environment especially helpful for English learners and students who are usually quieter.
Information Consumption:
Students engage with and respond to content created by their peers in real time. Teachers can add external resources like YouTube videos, Google Docs, or news articles to enrich learning. These boards turn into collaborative spaces where knowledge grows and ideas develop with every student contribution.
Impact on Learning:
Padlet has several positive effects on learning. It encourages critical thinking and creativity by allowing students to express themselves in different ways, supporting diverse learning styles. The platform also enables real time formative assessment, helping teachers monitor student understanding as it develops. However, there are challenges to using Padlet effectively. Without clear organization, boards can become cluttered, and students might go off topic or share nonacademic content. To address these issues, thoughtful moderation and clear guidelines for participation are essential to keep discussions focused and productive.
Privacy and Safety:
Padlet offers privacy settings like password-protected boards, visitor permissions, and content moderation. Teachers can restrict access to students with specific logins or email domains, and approve posts before they appear publicly.
Required Literacies:
Digital literacy involves navigating online platforms, uploading and embedding media, and solving access problems. Visual literacy is about understanding images and videos and creating visually appealing posts. Information literacy includes evaluating sources, citing them properly, and combining ideas from peers. Civic and communication literacy focuses on communicating respectfully, ethically, and inclusively in digital spaces.
Reflect on Implications:
Padlet aligns well with constructivist and student-centered teaching philosophies, promoting collaboration, inquiry, and creativity (Hobbs, 2017). It’s particularly effective for formative assessment, reflection journals, exit tickets, and group brainstorming. Educators should guide students in digital citizenship and media critique, while parents can help children think critically about what they post and how they interact online.
References
Google. (n.d.). Google Classroom. https://edu.google.com/products/classroom/
Google. (n.d.). Privacy & Security for Google for Education.
https://edu.google.com/why-google/privacy-security/
Google Classroom Workflow and Organization Tips and Tricks. (2020). Know Your Why! https://rechargelearning.blogspot.com/2020/03/google-classroom-workflow-and.html
Hobbs, R. (2017). Create to Learn: Introduction to Digital Literacy. Wiley-Blackwell.
How To Use Padlet And 5 Ways To Implement It Into Your Classroom - ClassPoint Blog. (2023, December 18). ClassPoint. https://www.classpoint.io/blog/how-to-use-padlet
Padlet. (n.d.). About Padlet. Retrieved June 21, 2025, from https://padlet.com/about
Padlet. (n.d.). Privacy Policy. Retrieved June 21, 2025, from https://padlet.com/about/privacy
Trust, T., & Whalen, J. (2020). Should teachers be trained in emergency remote teaching?
Lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Technology and Teacher
Education, 28(2), 189–199. https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/216179/